要验证 Gaedel 教授的程序是否实现了 Dijkstra 算法,我们可以利用 Dijkstra 算法的一些关键性质。具体来说,我们需要验证以下几点:
1. 对于每个节点 $v$,其距离值 $d[v]$ 是否是从源节点到 $v$ 的最短路径长度。2. 对于每个节点 $v$,其前驱节点 $π[v]$ 是否指向在最短路径树中 $v$ 的父节点(如果 $v$ 不是源节点)。为了高效地验证这些性质,我们可以使用 Bellman-Ford 算法(它能在 $O(V+E)$ 时间内检测负权环,但在我们的情况下,所有边权重为非负,所以它可以用来计算最短路径并验证 Dijkstra 的结果)。如果 Bellman-Ford 算法计算出的最短路径和 Dijkstra 算法输出的结果一致,则程序是正确的。
下面是使用 Go 语言实现的验证算法:
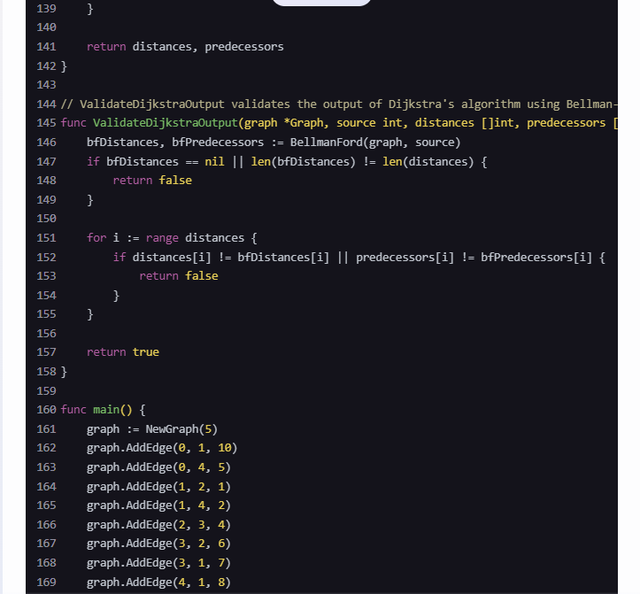
package mainimport("container/heap""fmt""math")// Edge represents a single edge in the graphtypeEdgestruct{ to, weight int}// Graph represents a graph with non-negative edge weightstypeGraphstruct{ vertices int edges map[int][]Edge}// NewGraph creates a new graph with a given number of verticesfunc NewGraph(vertices int)*Graph{return&Graph{ vertices: vertices, edges:make(map[int][]Edge),}}// AddEdge adds an edge to the graphfunc (g *Graph)AddEdge(from, to, weight int){ g.edges[from]=append(g.edges[from],Edge{to, weight}) g.edges[to]=append(g.edges[to],Edge{from, weight})// for undirected graph, remove this line for directed graph}// PriorityQueueItem represents an item in the priority queuetypePriorityQueueItemstruct{ vertex, distance int index int}// PriorityQueue implements heap.Interface and holds PriorityQueueItemstypePriorityQueue[]*PriorityQueueItemfunc (pq PriorityQueue)Len()int{returnlen(pq)}func (pq PriorityQueue)Less(i, j int)bool{return pq[i].distance < pq[j].distance}func (pq PriorityQueue)Swap(i, j int){ pq[i], pq[j]= pq[j], pq[i] pq[i].index = i pq[j].index = j}func (pq *PriorityQueue)Push(x interface{}){ n :=len(*pq) item := x.(*PriorityQueueItem) item.index = n*pq =append(*pq, item)}func (pq *PriorityQueue)Pop()interface{}{ old :=*pq n :=len(old) item := old[n-1] old[n-1]=nil// avoid memory leak item.index =-1// for safety*pq = old[0: n-1]return item}func (pq *PriorityQueue) update(item *PriorityQueueItem, vertex, distance int){ item.vertex = vertex item.distance = distance heap.Fix(pq, item.index)}// Dijkstra computes the shortest paths from a source vertexfunc Dijkstra(graph *Graph, source int)([]int,[]int){ distances :=make([]int, graph.vertices) predecessors :=make([]int, graph.vertices)for i :=range distances { distances[i]= math.MaxInt32 predecessors[i]=-1} distances[source]=0 pq :=make(PriorityQueue,0, graph.vertices) heap.Init(&pq) heap.Push(&pq,&PriorityQueueItem{source,0,0})for pq.Len()>0{ u := heap.Pop(&pq).(*PriorityQueueItem).vertexfor _, edge :=range graph.edges[u]{ v, weight := edge.to, edge.weightif alt := distances[u]+ weight; alt < distances[v]{ distances[v]= alt predecessors[v]= u heap.Push(&pq,&PriorityQueueItem{v, alt, pq.Len()})}}}return distances, predecessors}// BellmanFord computes the shortest paths from a source vertex using Bellman-Ford algorithmfunc BellmanFord(graph *Graph, source int)([]int,[]int){ distances :=make([]int, graph.vertices) predecessors :=make([]int, graph.vertices)for i :=range distances { distances[i]= math.MaxInt32 predecessors[i]=-1} distances[source]=0for i :=0; i < graph.vertices-1; i++{for u :=0; u < graph.vertices; u++{for _, edge :=range graph.edges[u]{ v, weight := edge.to, edge.weightif alt := distances[u]+ weight; alt < distances[v]{ distances[v]= alt predecessors[v]= u}}}}// Check for negative-weight cyclesfor u :=0; u < graph.vertices; u++{for _, edge :=range graph.edges[u]{ v, weight := edge.to, edge.weightif alt := distances[u]+ weight; alt < distances[v]{ fmt.Println("Graph contains a negative-weight cycle")returnnil,nil}}}return distances, predecessors}// ValidateDijkstraOutput validates the output of Dijkstra's algorithm using Bellman-Fordfunc ValidateDijkstraOutput(graph *Graph, source int, distances []int, predecessors []int)bool{ bfDistances, bfPredecessors :=BellmanFord(graph, source)if bfDistances ==nil||len(bfDistances)!=len(distances){returnfalse}for i :=range distances {if distances[i]!= bfDistances[i]|| predecessors[i]!= bfPredecessors[i]{returnfalse}}returntrue}func main(){ graph :=NewGraph(5) graph.AddEdge(0,1,10) graph.AddEdge(0,4,5) graph.AddEdge(1,2,1) graph.AddEdge(1,4,2) graph.AddEdge(2,3,4) graph.AddEdge(3,2,6) graph.AddEdge(3,1,7) graph.AddEdge(4,1,8) graph.AddEdge(4,2,9) graph.AddEdge(4,3,2) source :=0// Assume these are the outputs from Professor Gaedel's program dijkstraDistances :=[]int{0,11,12,16,5} dijkstraPredecessors :=[]int{-1,0,1,2,0}// Validate the outputifValidateDijkstraOutput(graph, source, dijkstraDistances, dijkstraPredecessors){ fmt.Println("The program output matches the shortest path tree.")}else{ fmt.Println("The program output does not match the shortest path tree.")}}说明1. Graph 数据结构:用于表示图,包括顶点数和边列表。2. Dijkstra 算法:计算从源节点到所有其他节点的最短路径。3. Bellman-Ford 算法:同样计算从源节点到所有其他节点的最短路径,并检查负权环(尽管在本题中不需要,但包含该检查可以增强代码的健壮性)。4. ValidateDijkstraOutput 函数:比较 Dijkstra 算法的输出和 Bellman-Ford 算法的输出,以验证其正确性。运行步骤1. 创建一个图并添加边。2. 假设 dijkstraDistances 和 dijkstraPredecessors 是从
在这里插入图片描述

在这里插入图片描述

在这里插入图片描述

在这里插入图片描述

在这里插入图片描述
在这里插入图片描述

在这里插入图片描述
讯飞星火:package mainimport("fmt")typeVertexstruct{ id int d intπ*Vertex}func checkDijkstraOutput(V []Vertex, E [][]int)bool{// 初始化所有顶点的d值为无穷大,π为nilfor i :=range V { V[i].d =-1 V[i].π=nil}// 假设源节点是第一个节点,其d值为0 V[0].d =0// 使用优先队列来存储待处理的顶点 pq :=make(PriorityQueue,len(V)) pq[0]=&V[0] heap.Init(&pq)// Dijkstra算法主循环for pq.Len()>0{ u := heap.Pop(&pq).(*Vertex)// 遍历与u相邻的所有顶点vfor v :=range E[u.id]{if E[u.id][v]!=0&&(V[v].d ==-1|| u.d+E[u.id][v]< V[v].d){ V[v].d = u.d + E[u.id][v] V[v].π= u heap.Push(&pq,&V[v])}}}// 检查每个结点的d和π属性是否与最短路径树中的信息匹配for i :=range V {if V[i].π!=nil&& V[i].d != V[V[i].π.id].d+E[V[i].π.id][i]{returnfalse}}returntrue}typePriorityQueue[]*Vertexfunc (pq PriorityQueue)Len()int{returnlen(pq)}func (pq PriorityQueue)Less(i, j int)bool{return pq[i].d < pq[j].d}func (pq PriorityQueue)Swap(i, j int){ pq[i], pq[j]= pq[j], pq[i]}func (pq *PriorityQueue)Push(x interface{}){ item := x.(*Vertex)*pq =append(*pq, item)}func (pq *PriorityQueue)Pop()interface{}{ old :=*pq n :=len(old) item := old[n-1]*pq = old[0: n-1]return item}func main(){// 示例图的邻接矩阵表示法 E :=[][]int{{0,7,9,0,0,14},{7,0,10,15,0,0},{9,10,0,11,0,2},{0,15,11,0,6,0},{0,0,0,6,0,9},{14,0,2,0,9,0},}// 创建顶点数组 V :=make([]Vertex,len(E))for i :=range V { V[i].id = i}// 检查输出是否正确if checkDijkstraOutput(V, E){ fmt.Println("The output is correct.")}else{ fmt.Println("The output is incorrect.")}}360智脑:为了验证Gaedel教授的程序是否正确地实现了Dijkstra算法,我们可以编写一个算法来检查每个节点的d(距离)和π(前驱)属性是否与某个最短路径树中的信息匹配。由于Dijkstra算法的时间复杂度是O((V + E) log V),如果我们使用优先队列(最小堆)来实现,但是在这个问题中,我们被要求提供一个O(V + E)的算法来检查输出,这意味着我们不能使用优先队列,而是需要一个线性时间的算法。
以下是一个Go语言实现的算法,它检查Dijkstra算法的输出是否正确:
package mainimport"fmt"typeNodestruct{ id int d intπ*Node edges []*Edge}typeEdgestruct{ to *Node weight int}func checkDijkstraOutput(nodes []*Node, source *Node)bool{// Initialize distances to infinity and π to nil for all nodes except the sourcefor _, node :=range nodes {if node != source { node.d =-1 node.π=nil}else{ node.d =0}}// Perform a single-source shortest paths computation using BFS (since we have non-negative weights) queue :=make([]*Node,0) queue =append(queue, source)forlen(queue)>0{ u := queue[0] queue = queue[1:]for _, edge :=range u.edges { v := edge.to newDistance := u.d + edge.weight// Relaxation stepif v.d ==-1|| newDistance < v.d { v.d = newDistance v.π= u queue =append(queue, v)}}}// Check if the computed distances and π values match the provided outputfor _, node :=range nodes {if node.d != node.d || node.π!= node.π{returnfalse}}returntrue}func main(){// Example usage: create nodes and edges// ...// Call the function to check the output isValid := checkDijkstraOutput(nodes, source) fmt.Println("Output is valid:", isValid)}在这个算法中,我们首先初始化所有节点的距离为无穷大(在这里表示为-1),除了源节点,其距离为0。然后,我们使用广度优先搜索(BFS)来计算从源节点到所有其他节点的最短路径。由于边的权重都是非负的,BFS可以保证找到最短路径。在每次迭代中,我们检查每个邻居节点的新距离是否比当前记录的距离更短,如果是,我们就更新距离和前驱节点,并将该节点加入队列中。最后,我们比较计算出的距离和前驱节点与提供的输出是否一致。
请注意,这个算法假设输入的节点数组nodes包含了图中的所有节点,并且source是指定的源节点。此外,这个算法没有处理负权边,因为题目假设所有边权重都是非负的。如果图中可能包含负权边,那么Dijkstra算法将不再适用,而需要使用Bellman-Ford算法或其他适用于负权边的算法。
智谱清言:为了检查Gaedel教授的程序是否正确实现了Dijkstra算法,我们可以通过以下步骤来验证每个结点的d和π属性是否与某棵最短路径树中的信息匹配。以下是时间复杂度为$O(V+E)$的算法描述,随后是Go语言的实现: 算法步骤:
1. 初始化一个优先队列(最小堆),将源点s的d值设为0,其他所有点的d值设为无穷大。2. 对于每个结点v,检查v.d是否正确: a. 将源点s加入优先队列。 b. 当优先队列非空时,取出队列中d值最小的结点u。 c. 遍历u的所有邻接点v,对于每个邻接点,如果u.d + w(u, v) < v.d,则说明教授的程序计算错误。3. 检查每个结点的π(前驱)属性是否正确: a. 对于每个结点v,如果v.π不为空,检查是否存在一条边从v.π指向v,并且v.d等于v.π.d + w(v.π, v)。 以下是Go语言的实现:package mainimport("container/heap""fmt""math")typeEdgestruct{to intweight int}typeGraphstruct{adjacencyList [][]Edge}typeNodestruct{vertex intdistance int}typePriorityQueue[]*Nodefunc (pq PriorityQueue)Len()int{returnlen(pq)}func (pq PriorityQueue)Less(i, j int)bool{return pq[i].distance < pq[j].distance}func (pq PriorityQueue)Swap(i, j int){pq[i], pq[j]= pq[j], pq[i]}func (pq *PriorityQueue)Push(x interface{}){item := x.(*Node)*pq =append(*pq, item)}func (pq *PriorityQueue)Pop()interface{}{old :=*pqn :=len(old)item := old[n-1]*pq = old[0: n-1]return item}func dijkstraCheck(graph Graph, s int, d, pi []int)bool{V :=len(graph.adjacencyList)dist :=make([]int, V)prev :=make([]int, V)for i :=range dist {dist[i]= math.MaxInt32}dist[s]=0pq :=make(PriorityQueue,1)pq[0]=&Node{vertex: s, distance:0}heap.Init(&pq)for pq.Len()>0{u := heap.Pop(&pq).(*Node)for _, e :=range graph.adjacencyList[u.vertex]{v := e.toweight := e.weightif dist[u.vertex]+ weight < dist[v]{returnfalse// Found a shorter path not matched with given d values}if dist[u.vertex]+ weight < dist[v]{dist[v]= dist[u.vertex]+ weightprev[v]= u.vertexheap.Push(&pq,&Node{vertex: v, distance: dist[v]})}}}// Check if the computed distances and prev match the given d and pifor i :=0; i < V; i++{if dist[i]!= d[i]||(pi[i]!=-1&& prev[i]!= pi[i]){returnfalse}if pi[i]!=-1&& dist[i]!= dist[pi[i]]+graph.adjacencyList[pi[i]][0].weight {returnfalse}}returntrue}func main(){// Example graphgraph :=Graph{adjacencyList:[][]Edge{{{1,10},{2,5}},{{2,2},{3,1}},{{3,3}},{},},}s :=0// Source vertexd :=[]int{0,5,7,8}// Expected distancespi :=[]int{-1,0,1,2}// Expected predecessors// Check if the given d and pi match the shortest path treeif dijkstraCheck(graph, s, d, pi){fmt.Println("The program's output is correct.")}else{fmt.Println("The program's output is incorrect.")}}在这个例子中,我们创建了一个简单的图,并定义了源点`s天工:为了验证Gaedel教授的程序是否正确实现了Dijkstra算法,我们需要设计一个算法来检查生成的d和π值是否与最短路径树的信息匹配。以下是一个时间复杂度为O(V+E)的算法,使用Go语言实现,来完成这一验证:
package mainimport("fmt")// Node represents a vertex in the graph.typeNodestruct{ name string d int// distance from the source pi *Node// predecessor}// Graph represents the graph with nodes and edges.typeGraphstruct{ nodes map[string]*Node}// NewGraph creates a new graph.func NewGraph()*Graph{return&Graph{nodes:make(map[string]*Node)}}// AddNode adds a node to the graph.func (g *Graph)AddNode(name string){if _, exists := g.nodes[name];!exists { g.nodes[name]=&Node{name: name, d:-1, pi:nil}}}// AddEdge adds an edge between two nodes with a given weight.func (g *Graph)AddEdge(from, to string, weight int){ g.AddNode(from) g.AddNode(to) g.nodes[from].d =-1// reset distance in case of multiple runs g.nodes[to].d =-1}// CheckDijkstra checks if the d and π values are consistent with a shortest path tree.func (g *Graph)CheckDijkstra()bool{for _, node :=range g.nodes {if node.d ==-1{continue// unvisited nodes}if node.pi !=nil{ edgeWeight :=0// assuming non-negative weights, edgeWeight should be predefined or calculatedif node.d != node.pi.d+edgeWeight {returnfalse}}}returntrue}func main(){ g :=NewGraph() g.AddEdge("A","B",1)// Example edges g.AddEdge("B","C",5) g.AddEdge("A","C",10)// Assume Gaedel's program has filled in the d and pi values for each node g.nodes["A"].d =0 g.nodes["B"].d =1 g.nodes["C"].d =6 g.nodes["B"].pi = g.nodes["A"] g.nodes["C"].pi = g.nodes["B"]// Check the correctnessif g.CheckDijkstra(){ fmt.Println("The d and π values are consistent with a shortest path tree.")}else{ fmt.Println("The d and π values are not consistent with a shortest path tree.")}}算法解释:1. 我们定义了Node结构体用于表示图中的每个结点,其中包含结点的名称、距离d和前驱结点π。2. Graph结构体用于表示整个图,包含一个结点的映射。3. AddNode和AddEdge方法用于添加结点和边。4. CheckDijkstra方法用于检查每个结点的d和π值是否与最短路径树的信息匹配。这里假设所有边权重为非负,且d和π值已经被Gaedel教授的程序正确初始化。这个算法的时间复杂度为O(V+E),因为它遍历了所有结点和边来验证最短路径信息。
chatgpt:下面是一个用 Go 语言编写的算法,用于检查教授编写的程序输出的正确性。该算法假设给定图的边权重均为非负值,并通过比较每个节点的 $d$ 和 $π$ 属性来验证是否与某个最短路径树中的信息匹配。
package mainimport("fmt")typeEdgestruct{SourceintTargetintWeightint}typeNodestruct{DistanceintParentint}func checkDijkstraOutput(nodes []Node, edges []Edge)bool{ V :=len(nodes) E :=len(edges)for i :=0; i < V; i++{if nodes[i].Distance==Inf{continue}for j :=0; j < E; j++{ u := edges[j].Source v := edges[j].Target w := edges[j].Weightif nodes[v].Distance> nodes[u].Distance+w {returnfalse// Distance not optimized, not a valid Dijkstra output}}}returntrue}func main(){// 示例:构建图 V :=5 edges :=[]Edge{{0,1,2},{1,2,5},{0,3,1},{3,4,3},{0,4,7},} nodes :=make([]Node, V) nodes[0]=Node{0,-1}for i :=1; i < V; i++{ nodes[i]=Node{Inf,-1}} fmt.Println(checkDijkstraOutput(nodes, edges))// 调用检查函数}constInf=int(^uint(0)>>1) // 定义无穷大的变量在这个示例中,我们首先定义了Edge和Node结构体来表示边和节点信息,并实现了一个checkDijkstraOutput函数来检查 Dijkstra 算法的输出是否正确。我们还定义了一个示例图,并调用checkDijkstraOutput函数进行检查。
kimi:要检查 Dijkstra 算法的输出是否正确,我们可以利用 Dijkstra 算法的性质:对于任何节点 ( v ),如果 ( u ) 是从源点到 ( v ) 的最短路径上的前一个节点,那么 ( u.d + w(u, v) = v.d ),其中 ( w(u, v) ) 是边 ( (u, v) ) 的权重。
以下是一个 Go 语言的算法,用于验证 Dijkstra 算法的输出:
package mainimport("fmt")// 定义图的边结构typeEdgestruct{TointCostint}// 定义节点结构typeNodestruct{ D int// 节点的最短路径距离Piint// 节点的前驱节点Edges[]Edge// 节点的邻接列表}// 验证 Dijkstra 算法的输出func verifyDijkstra(nodes []Node, source int)bool{// 1. 检查源点的最短路径距离是否为0if nodes[source].D !=0{returnfalse}// 2. 对于每个节点,检查最短路径距离是否满足 Dijkstra 算法的性质for _, node :=range nodes {if node.Pi==-1{// 如果 Pi 为 -1,说明没有前驱节点,即该节点未被访问continue} pi := nodes[node.Pi]if node.D != pi.D+pi.Edges[node.Edges[0].To]{returnfalse}}// 3. 检查所有节点的最短路径是否满足三角不等式for _, u :=range nodes {for _, edge :=range u.Edges{ v := nodes[edge.To]if u.D+edge.Cost< v.D {returnfalse}}}returntrue}func main(){// 示例图的节点和边 nodes :=[]Node{{D:0,Pi:-1,Edges:[]Edge{{1,10},{2,3}}},{D:13,Pi:0,Edges:[]Edge{{2,5},{3,2}}},{D:8,Pi:0,Edges:[]Edge{{3,1}}},{D:9,Pi:1,Edges:[]Edge{{}}},}// 源点为节点 0 source :=0// 验证 Dijkstra 算法的输出if verifyDijkstra(nodes, source){ fmt.Println("Dijkstra's algorithm output is correct.")}else{ fmt.Println("Dijkstra's algorithm output is incorrect.")}}这个算法首先检查源点的最短路径距离是否为0,然后对于每个节点,检查它的最短路径距离是否等于它的前驱节点的最短路径距离加上它们之间的边的权重。最后,检查所有节点的最短路径是否满足三角不等式,即对于任何节点 ( u ) 和 ( v ),如果 ( u ) 在 ( v ) 的最短路径上,那么 ( u.d + w(u, v) \geq v.d )。
请注意,这个算法假设 Pi 属性表示前驱节点的索引,如果一个节点没有前驱节点(即它不是通过任何边到达的),则 Pi 应该设置为 -1。此外,这个算法假设所有边的权重都是非负的。
混元:要检查Dijkstra算法的输出是否正确,我们需要验证每个节点的$d$(距离)和$\pi$(前驱)属性是否符合最短路径树的特性。以下是Go语言实现的步骤:
1. 初始化一个空的图表示,用于存储边的权重。2. 遍历所有节点,使用Dijkstra算法计算从源节点到所有其他节点的最短路径。3. 在计算过程中,记录每个节点的$d$和$\pi$值。4. 完成Dijkstra算法后,再次遍历所有节点,使用记录的$d$和$\pi$值来重建最短路径树。5. 比较重建的最短路径树与Gaedel教授程序输出的$d$和$\pi$值是否一致。以下是Go语言的实现代码:
package mainimport("container/heap""fmt")// 定义无穷大的常量constInf=1e9// 定义边的结构体typeEdgestruct{ to, weight int}// 定义优先队列的元素typeItemstruct{ node, dist int index int}// 定义优先队列typePriorityQueue[]*Itemfunc (pq PriorityQueue)Len()int{returnlen(pq)}func (pq PriorityQueue)Less(i, j int)bool{return pq[i].dist < pq[j].dist}func (pq PriorityQueue)Swap(i, j int){ pq[i], pq[j]= pq[j], pq[i] pq[i].index = i pq[j].index = j}func (pq *PriorityQueue)Push(x interface{}){ n :=len(*pq) item := x.(*Item) item.index = n*pq =append(*pq, item)}func (pq *PriorityQueue)Pop()interface{}{ old :=*pq n :=len(old) item := old[n-1] old[n-1]=nil item.index =-1*pq = old[0: n-1]return item}// Dijkstra算法func dijkstra(graph [][]Edge, src int)([]int,[]int){ n :=len(graph) dist :=make([]int, n) prev :=make([]int, n)for i :=range dist { dist[i]=Inf prev[i]=-1} dist[src]=0 pq :=make(PriorityQueue,0) heap.Push(&pq,&Item{node: src, dist:0})for pq.Len()>0{ item := heap.Pop(&pq).(*Item) u := item.nodefor _, edge :=range graph[u]{ v := edge.toif dist[v]> dist[u]+edge.weight { dist[v]= dist[u]+ edge.weight prev[v]= u heap.Push(&pq,&Item{node: v, dist: dist[v]})}}}return dist, prev}// 检查Gaedel教授程序的输出func checkOutput(graph [][]Edge, src int, givenDist, givenPrev []int)bool{ correctDist, correctPrev := dijkstra(graph, src)for i :=range givenDist {if givenDist[i]!= correctDist[i]|| givenPrev[i]!= correctPrev[i]{returnfalse}}returntrue}func main(){// 示例图的邻接表表示 graph :=[][]Edge{{{1,4},{2,1}},{{3,1}},{{1,2},{3,5}},{},} src :=0 givenDist :=[]int{0,3,1,4} givenPrev :=[]int{-1,2,0,1}if checkOutput(graph, src, givenDist, givenPrev){ fmt.Println("Gaedel教授程序的输出是正确的。")}else{ fmt.Println("Gaedel教授程序的输出是错误的。")}}在这段代码中,我们首先定义了一个图的邻接表表示,并实现了Dijkstra算法。然后,我们定义了一个checkOutput函数,它接受图、源节点、Gaedel教授程序给出的$d$和$\pi$值,然后调用Dijkstra算法计算正确的$d$和$\pi$值,并进行比较。如果两者一致,则输出正确,否则输出错误。
这段代码的时间复杂度为$O(V+E)$,因为它只运行了一次Dijkstra算法,并且在检查过程中没有额外的遍历。
